|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Whether you’re just starting your journey with Microsoft Excel or want a refresher, this post will walk you through everything you need to know about Excel’s layout, key components, and how things work behind the scenes.
If you haven’t already, check out our previous post on What is Excel? – Introduction, History & Use Cases to get a strong foundation before diving into the overview.
What is Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet application developed by Microsoft. It’s designed to help users manage, analyze, and visualize data. Whether you’re working with simple tables or complex formulas, Excel provides a flexible environment to organize and manipulate information.
Excel Interface – First Look
When you open Excel, you’re greeted with a clean and organized screen. Here’s a breakdown of the key areas you see:
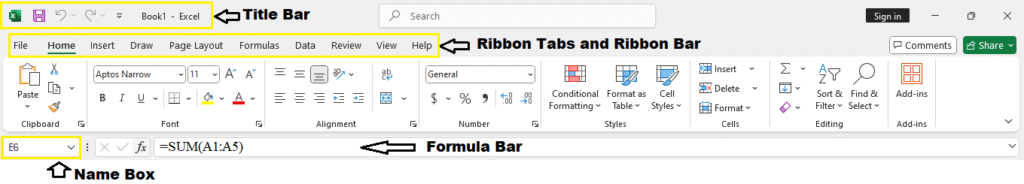
1. Title Bar
- Displays the name of the file and the app.
- Shows the “Save,” “Undo,” and “Redo” icons.
2. Ribbon Tabs and Ribbon Bar
- Contains all the tools organized under tabs like Home, Insert, Page Layout, Formulas, Data, etc.
- Each tab opens a different set of tools grouped logically.
3. Formula Bar
- Shows what’s inside the selected cell (value or formula).
- You can enter or edit cell content directly here.
4. Name Box
- Located to the left of the formula bar.
- Displays the cell name or range you’ve selected.
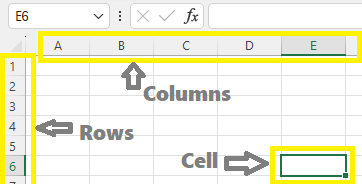
5. Worksheet Area
- This is where the actual data entry happens.
- It’s made of columns (A, B, C,…) and rows (1, 2, 3,…), creating cells (like A1, B2 or E6).
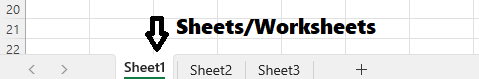
6. Sheet Tabs
- At the bottom, you’ll see “Sheet1”, “Sheet2”, etc.
- You can rename, add, or delete sheets as per your need.
Understanding Excel File Structure
- Workbook: An Excel file is called a workbook. It can contain one or more sheets (worksheets).
- Worksheet: Each sheet inside the workbook where you enter data.
- Cell: A single box where you can enter data, formulas, or functions.
- Range: A selection of multiple cells (e.g., A1:A10).
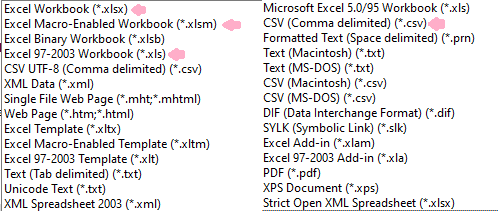
Excel File Extensions
| Extension | Purpose |
|---|---|
.xlsx | Default Excel workbook (no macros) |
.xlsm | Macro-enabled workbook |
.xls | Older Excel format (2003 and before) |
.csv | Comma-separated values file |
How Excel Works Behind the Scenes
- Excel recalculates formulas instantly when data changes.
- Built-in functions help automate calculations.
- Data can be formatted using colors, styles, and number formats for better visibility.
Key Features at a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
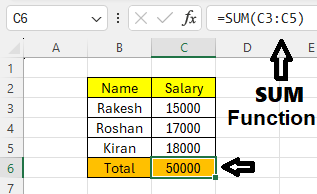
| Formulas & Functions | Automate calculations like SUM, AVERAGE, IF, VLOOKUP |
| Charts | Visualize your data with Bar, Line, Pie, etc. |
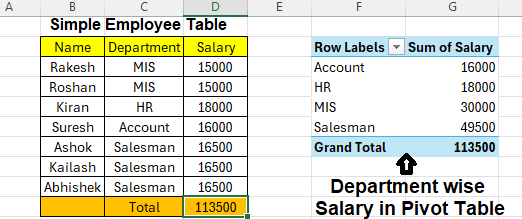
| Pivot Tables | Summarize large data sets |
| Data Validation | Control what type of data goes into a cell |
| Sorting & Filtering | Organize and view specific data easily |
Final Tips Before You Start
- Practice using Excel daily, even for small tasks.
- Don’t memorize all formulas – understand how they work.
- Use real-life examples like monthly budgets, attendance sheets, or inventory logs to practice.
What’s Next?
In our next post, we’ll dive into Excel Ribbon Tabs — A Beginner’s Guide!
Stay tuned, and don’t forget to bookmark this guide for reference