|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
If you’re just starting out with Excel and wondering how to add numbers quickly, you’re in the right place! In this post, we’ll show you how to use the Excel SUM Function step-by-step — from creating a new workbook to saving your work like a pro.
Let’s begin!
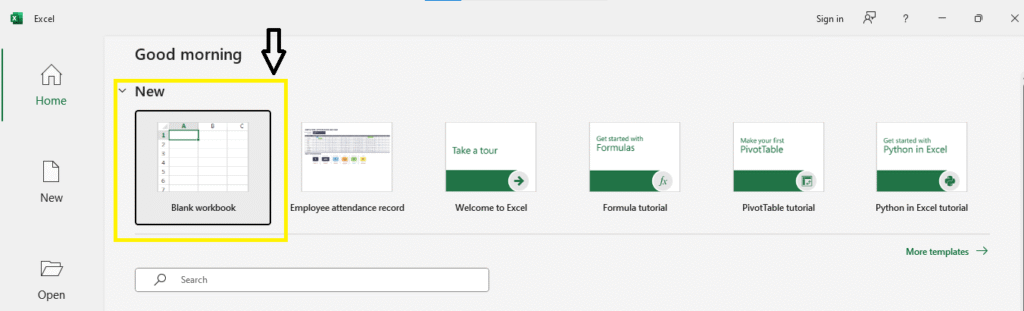
1. Open Excel and Create a New Workbook
- Open Microsoft Excel.
- You’ll see options like “Blank Workbook” — click on it.
- Now you have a fresh, empty sheet where we’ll work.
2. Entering Data into Cells
Let’s say you want to add some numbers — like daily expenses or marks.
Example:
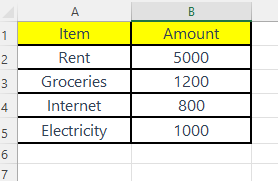
| A | B |
|---|---|
| Item | Amount |
| Rent | 5000 |
| Groceries | 1200 |
| Internet | 800 |
| Electricity | 1000 |
Here’s how to do it:
- Click on cell A1, type
Item, press Enter. - In B1, type
Amount, then press Enter. - Fill the rest as shown above by clicking one cell at a time.
3. Basic Formatting (Make it Look Nice)
Let’s make your sheet clear and clean:
- Bold headers (A1 and B1): Select the cells → press Ctrl + B or click Bold from the toolbar.
- Add borders to your table: Select A1 to B5 → click on Borders in the Home tab → choose “All Borders”.
- You can also center align the text and change font color if you like.
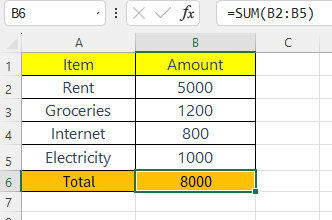
4. Use the SUM Function – Let Excel Add for You!
Now let’s use the SUM function to calculate the total expenses.
Method 1: Basic SUM Formula
Click on B6 (just below the last amount), and type:
=SUM(B2:B5)
Then press Enter.
Excel will add all the numbers from B2 to B5 and show the total in B6.
Method 2: AutoSum (No Typing!)
- Click on B6.
- Go to the Home tab → Click AutoSum (∑) or use shortcut (Alt+=).
- Excel will automatically select B2 to B5. Press Enter.
Method 3: SUM for Non-Continuous Cells
If your numbers are not in a single block (e.g., B2, B4, B6), you can write:
=SUM(B2, B4, B6)
This adds only the selected cells.
Method 4: SUM Across Rows
You can also use SUM across a row.
Example:
=SUM(A2:E2)
This adds all numbers in Row 2 between columns A to E.
5. Save Your File Properly
Don’t lose your work!
- Click File > Save As
- Choose a folder (like Desktop or Documents)
- Name your file, like:
MyFirstExcelSUM.xlsx - Click Save
Summary
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Workbook | Open Excel and start a blank sheet |
| Enter Data | Fill in numbers and headings |
| Format Sheet | Bold, borders, align, color |
| Use SUM Formula | =SUM(range) to quickly add numbers |
| Save the Workbook | Save with a clear file name and folder |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the primary purpose of the SUM function in Excel?
The primary purpose of the SUM function in Excel is to add two or more numbers together. It helps you quickly calculate totals for things like expenses, marks, or sales, using a simple formula like =SUM(A1:A5).
Q2. How to use sum function in Excel?
To use the SUM function, click the cell where you want the total, type =SUM(range) and press Enter.
Example: =SUM(B2:B5) will add all numbers from cell B2 to B5
Q3. What is the shortcut for using SUM in Excel?
You can quickly use the SUM function with the shortcut:
Select the empty cell below your numbers and press Alt + =, then press Enter. Excel will automatically calculate the total.
Q4. Why am I getting a #VALUE! error in the SUM function?
This error usually means one or more cells contain text that can’t be converted into a number. Double-check your range to ensure all values are numeric.
Q5. Does the SUM function ignore text and blank cells?
Yes, Excel automatically ignores any text or blank cells inside the range. It only adds cells that contain numbers.
What’s Next?
Now that you know how to use the SUM function, try it with your own data — like monthly expenses, marks, or sales.
In the next post, learn about the AVERAGE function — to find out how much you spend or score on average.