|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
When learning Python, one of the most exciting moments is when your code starts interacting with you — asking questions, taking answers, and responding back. This magic is done through input and output in Python.
In this post, we’ll explore how to:
- Display messages using
print() - Take input from the user using
input() - Format output in clean and professional ways
- Practice with real-life examples
Let’s dive into the conversation between you and your code!
What is Output in Python?
Output simply means showing something on the screen.
In Python, we use the built-in function print() to display output.
Basic Syntax:
print("Hello, SmartTejas!")This will show:
Hello, SmartTejas!You can also print numbers and variables:
name = "Tejas"
age = 29
print(name)
print(age)Output:
Tejas
29Also Read: Python Variables and Data Types
Printing Multiple Items
You can print multiple items by separating them with commas.
name = "Tejas"
age = 29
print("Name:", name, "Age:", age)This will print:

👉 Python automatically adds a space between each item.
Formatting Output
Want your output to look cleaner or more professional? You can format strings using f-strings, which were introduced in Python 3.6.
Using f-strings:
name = "Raj"
marks = 87.5
print(f"{name} scored {marks} marks in the exam.")Output:
Raj scored 87.5 marks in the exam.This is very useful when combining text with variables.
What is Input in Python?
Now let’s make the program ask you something.
We use the input() function to take input from the user. This input is always taken as a string.
Basic Example:
name = input("Enter your name: ")
print("Hello", name)When this runs, the user sees:
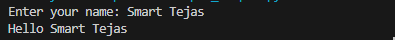
👉 Remember: Input is always a string.
Even if the user enters a number, it will be stored as text. You’ll need to convert it usingint()orfloat().
Converting Input to Numbers
Example: Add Two Numbers
num1 = input("Enter first number: ")
num2 = input("Enter second number: ")
# Convert to integers
num1 = int(num1)
num2 = int(num2)
total = num1 + num2
print("The sum is:", total)If the user enters 10 and 20, the output will be:
The sum is: 30Without conversion, it would have joined the strings like:
1020So type conversion is important for numerical operations.
Real-Life Example: Student Report Card
name = input("Enter student name: ")
math = float(input("Enter marks in Math: "))
science = float(input("Enter marks in Science: "))
average = (math + science) / 2
print(f"\nStudent: {name}")
print(f"Average Marks: {average}")Sample Output:
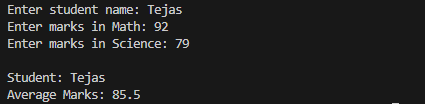
Use \n and \t for Formatting
These are escape characters that help improve the look of your output.
\n→ New line\t→ Tab space
Example:
print("Subject\tMarks")
print("Math\t90")
print("Science\t85")Output:
Subject Marks
Math 90
Science 85
Quick Practice Challenge
Write a program that:
- Asks the user for their name
- Asks for two numbers
- Prints a greeting and the product of the numbers
Hint:
- Use
input() - Convert to
intorfloat - Use
f-stringsto format output
FAQs – Input and Output in Python
Is user input always a string in Python?
Yes. Whatever you enter using input() is stored as a string.
If you need a number, convert it:
How do I print multiple values in one line?
Use commas in print():
print(f"The values are {x} and {y}") #using f-string
How do I change the separator in print()?
Use the sep parameter:
How do I print without a new line?
By default, print() adds a new line. Use end to change it:
Can I take multiple inputs in one line?
Yes, using split():
Summary
| Function | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
print() | Display output | Add f"" for formatted output |
input() | Take user input | Always returns a string |
int(), float() | Convert input types | Use before math operations |
Mastering input and output is like learning how to talk to your code. It’s the foundation of every interactive program you’ll build in Python.
What’s Next?
In the next post, we’ll learn about the Operators in Python