|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Master Pivot Table in Excel from basic to advanced. Learn how to summarize, analyze, and visualize data effectively using real-world examples.
If you work with large amounts of data in Excel, manually analyzing it can be time-consuming and error-prone. This is where Pivot Tables come in. With just a few clicks, Pivot Tables help you summarize and analyze data efficiently.
Whether you’re a beginner or looking to level up your skills, this guide will teach you how to use Pivot Tables from basic to advanced – with step-by-step instructions, real-life sales examples.
What is a Pivot Table?
A Pivot Table is a tool in Excel that allows you to:
- Summarize large datasets
- Group and filter data dynamically
- Calculate totals, averages, percentages, and more
It’s one of the most powerful features in Excel for reporting and decision-making.
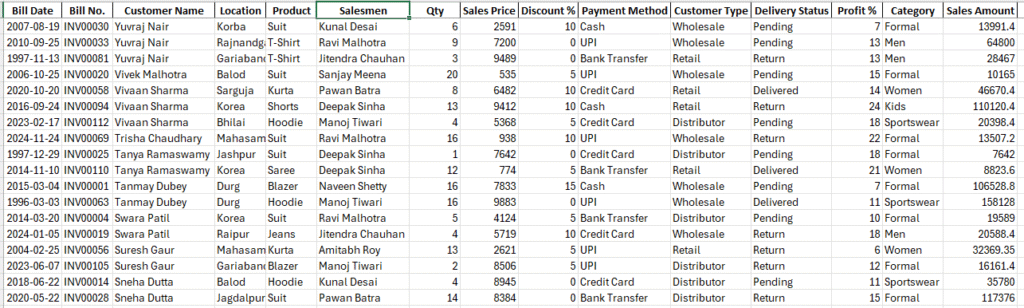
Sample Dataset Used in This Guide
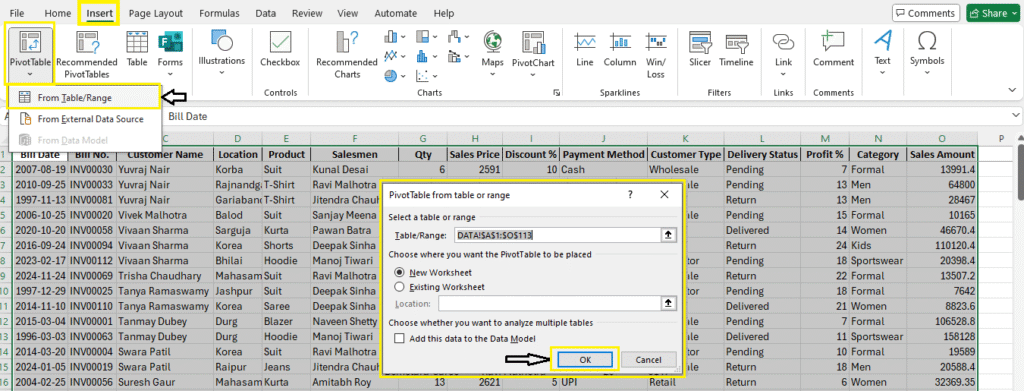
How to Insert a Pivot Table
- Select your data range (e.g., A1:F113)
- Go to the
Inserttab - Click
PivotTableor (use shortcut: Alt+N+V then press Enter Key) - Choose whether to place it in a New Worksheet or an Existing Worksheet
- Click OK
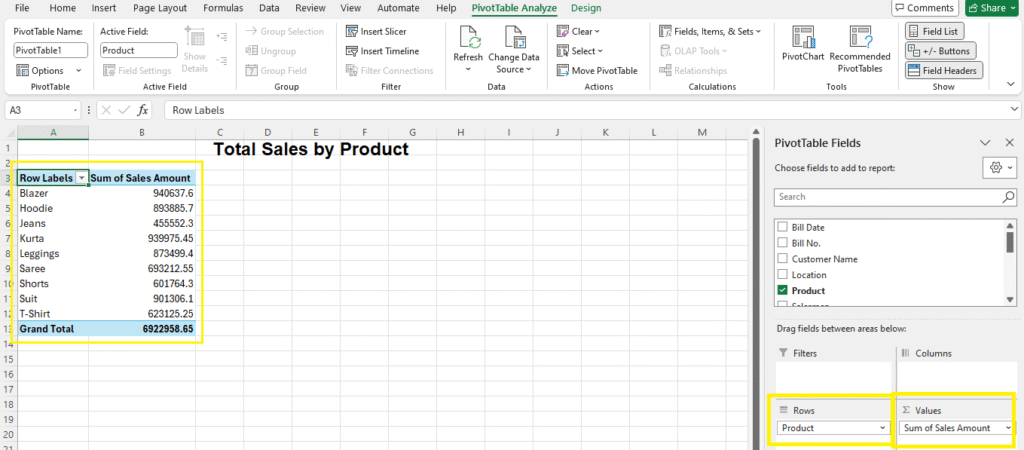
Example 1: Total Sales by Product
Steps:
- Drag
Productto Rows - Drag
Sales Amountto Values
Result:
| Product | Sum of Sales Amount |
| Blazer | 940637.6 |
| Hoodie | 893885.7 |
| Jeans | 455552.3 |
| Kurta | 939975.45 |
Read More: VLOOKUP in Excel and SUMIF & SUMIFS in Excel
Grouping Data: Group by Location or Customer
Example 2: Total Sales by Location with Filter
- Drag
Locationto Rows - Drag
Sales Amountto Values
Filter data in Pivot Table:
Filters are used to select what data you see.
In this example, there are two filters enabled: Salesmen and Delivery Status.
The filters are set to:
Salesmen = Naveen Shetty and
Delivery Status = Delivered.
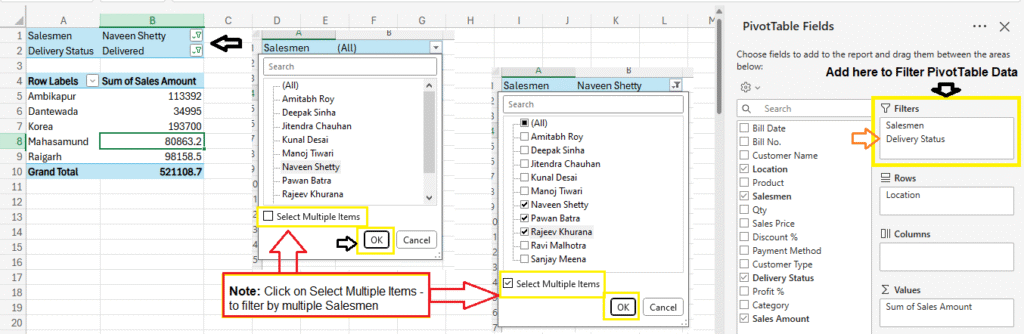
Note: Click on Select Multiple Items – to filter by multiple Salesmen
Example 3: Total Sales by Customer
- Drag
Customer Nameto Rows - Drag
Sales Amountto Values
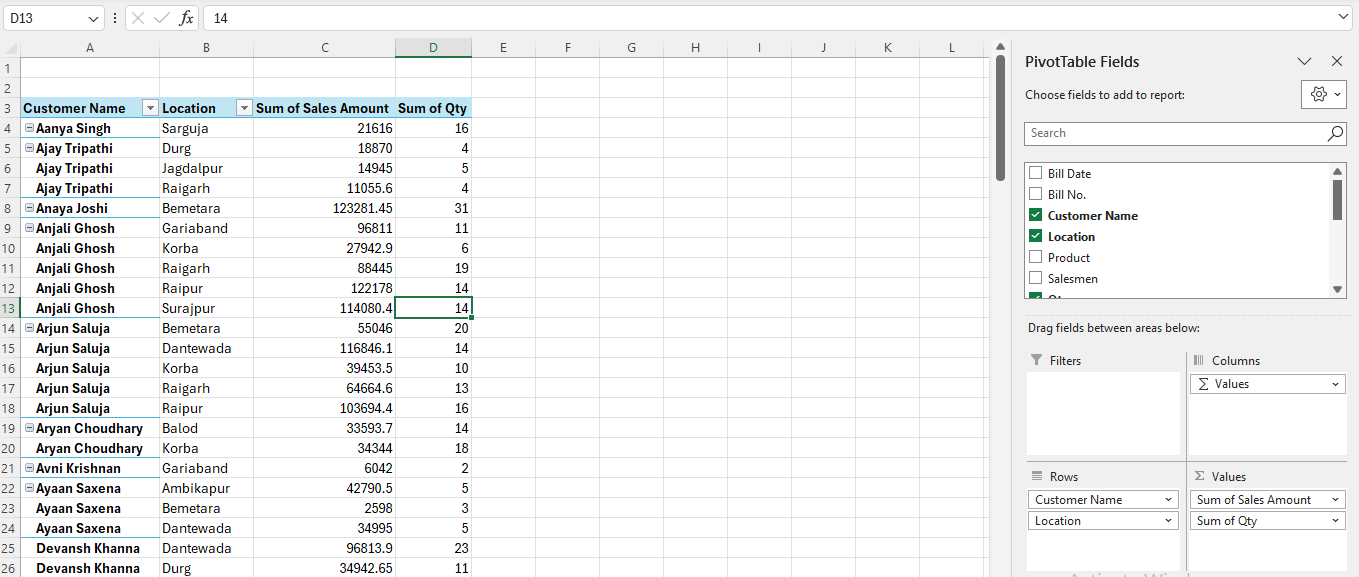
Example 4: Total Sales Amount and Qty by Customer and Location
Steps:
- Drag Customer and Location to Rows
- Sales Amount and Qty to Values
Now Your Table will look like this:
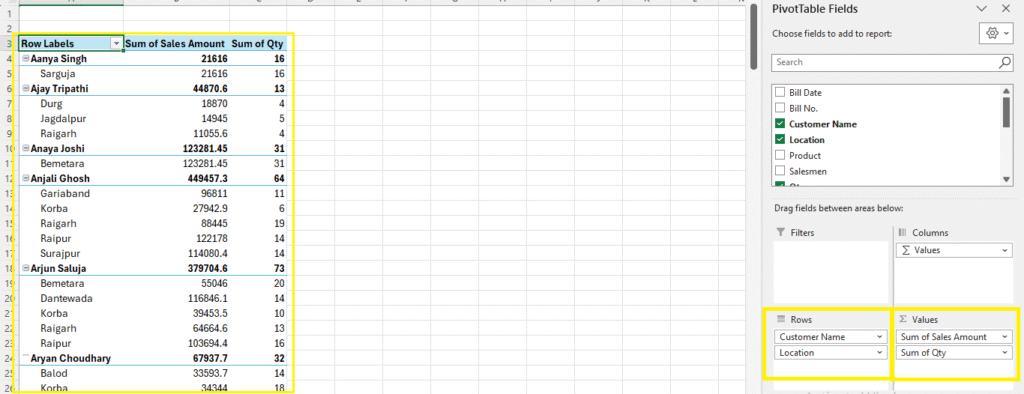
Step 2: Let’s convert this data to Tabular Form, meaning:
- Customer Name in Column A,
- Location in Column B
- Sales Amount in Column C and Qty in Column D
- Click anywhere in Pivot Table and go to Design Tab, then follow bellow steps:
Step 1: Design Tab > Report Labout > Show in Tabular Form
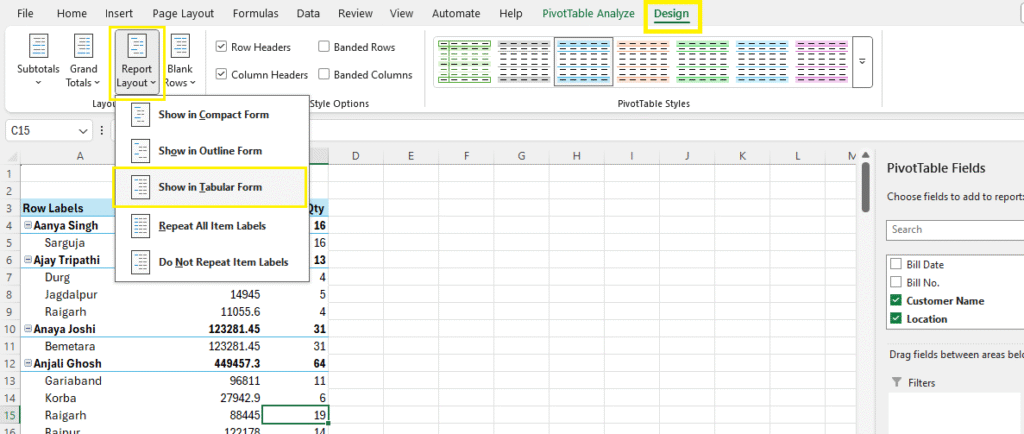
Step 2: Design Tab > Subtotals > Do Not Show Subtotals
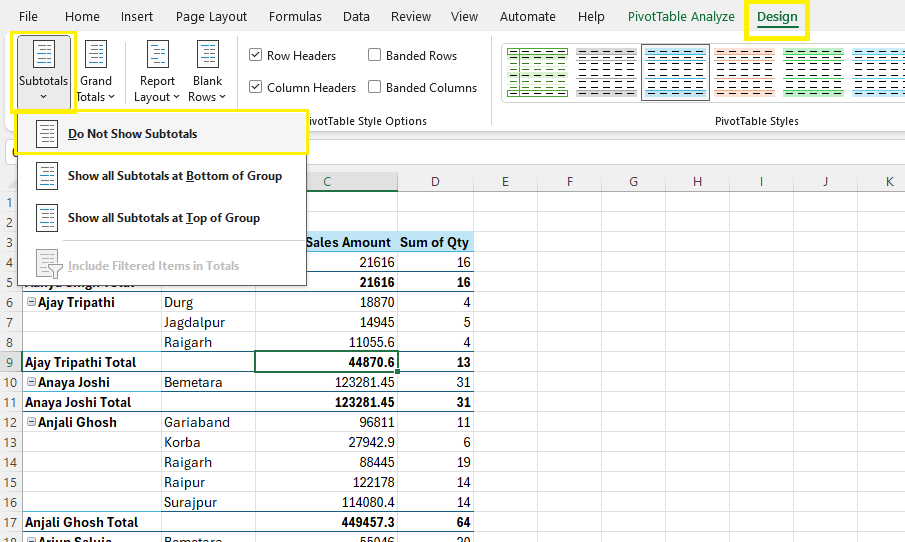
Step 3: Design Tab > Report Layout > Repeat All Item Labels
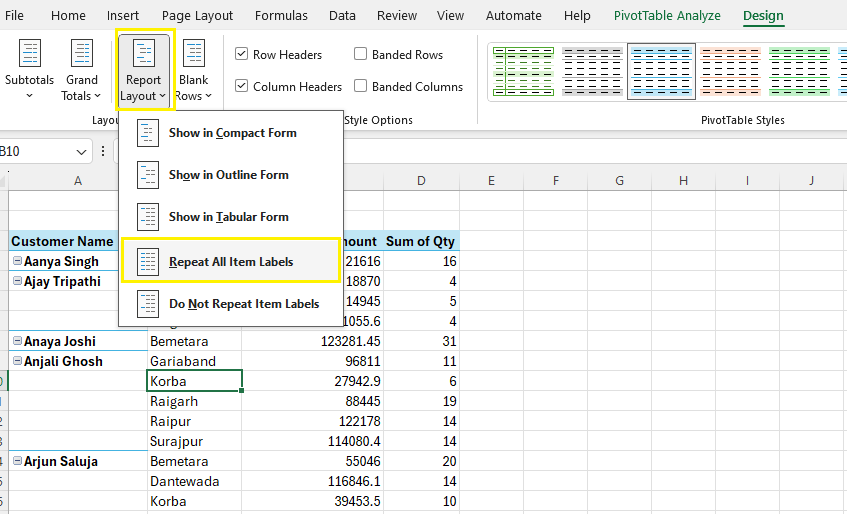
Final Output:
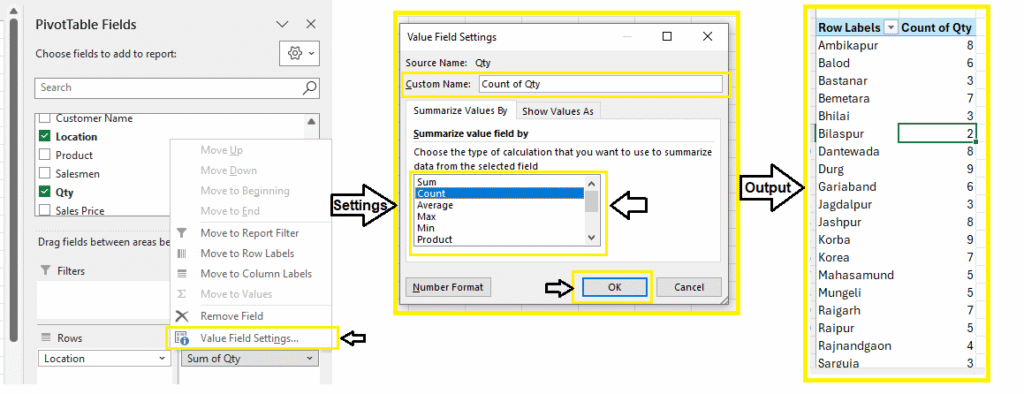
Custom Calculations in Pivot Table
You can add:
- Count instead of sum
- Averages
- Max, Min
Steps:
- Click the dropdown in Values →
Value Field Settings - Choose
Average,Count, etc.
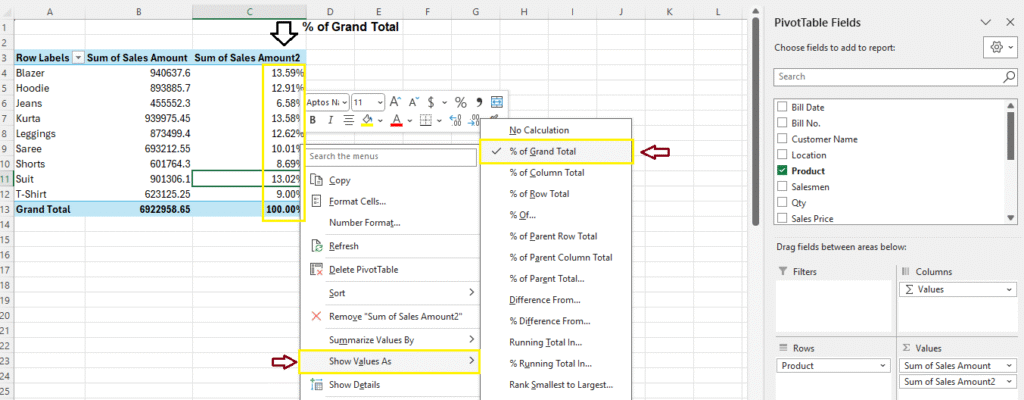
Advanced Pivot Table Techniques
1. Show % of Total Sales – Contribution of Each Row in 100%
Show how much each product contributes to total sales.
- Right-click Sales Amount field
- Choose
Show Values As > % of Grand Total
2. Create Pivot Charts
Go to PivotTable Analyze > PivotChart
- Create Bar, Column, Pie, etc.
Note: We will learn all about Charts & Pivot Charts in a separate tutorial.
3. Use Slicers to Filter Pivot Tables
Slicers are visual filters.
- Go to
Insert > Slicer - Select fields like Location or Product
Note: Slicers in Pivot Tables are used to filter data quickly and easily with clickable buttons visually.
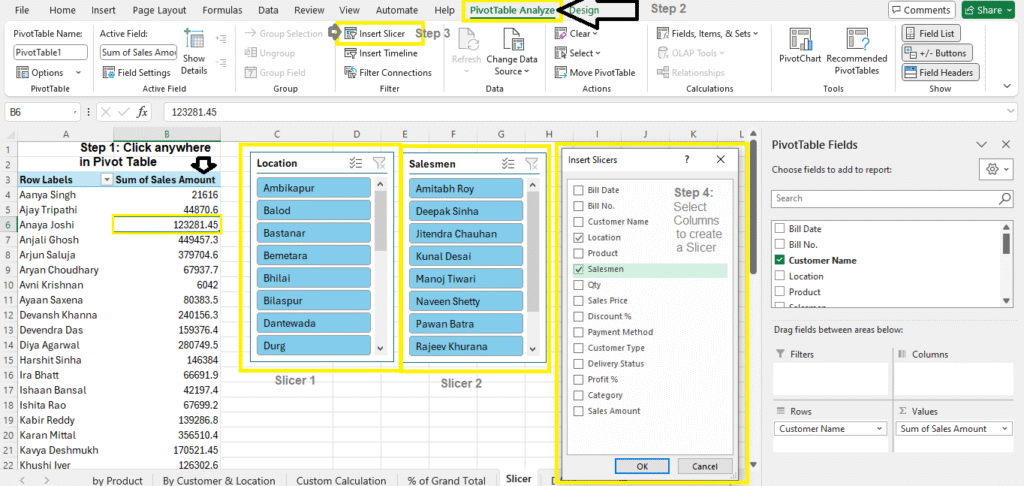
Note: Click on Slicer to Change it’s Settings (under Slicer Tab)
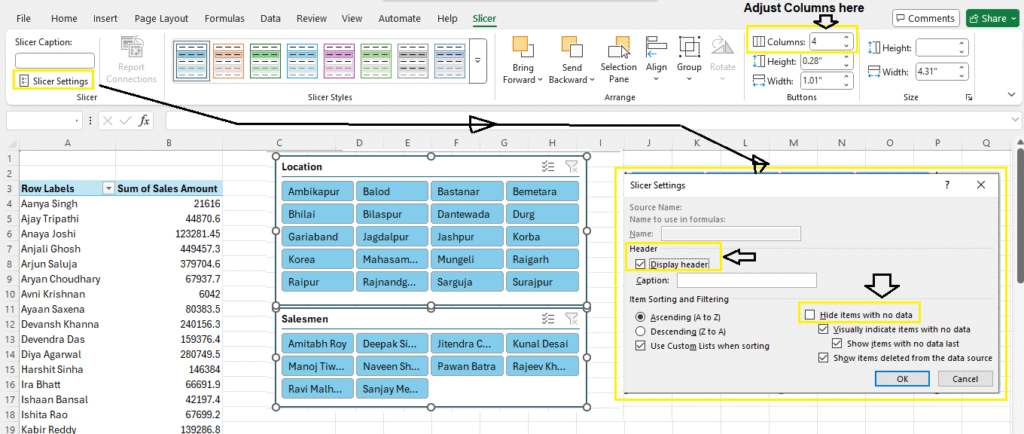
4. Add Multiple Value Fields
You can drag Qty and Sales Amount to Values to show both.
Note: For Practice
Real-Life Example Scenarios
Example 1: Compare Sales by Location
- Rows: Location
- Values: Sales Amount
Example 2: Count of Orders by Product
- Rows: Product
- Values: Bill No (set to Count)
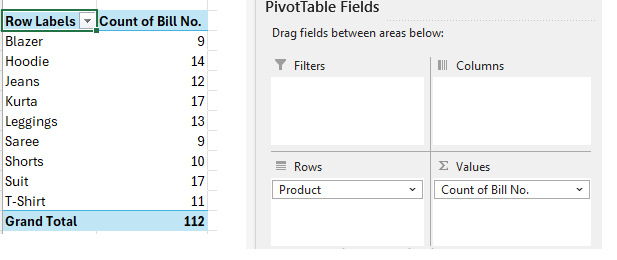
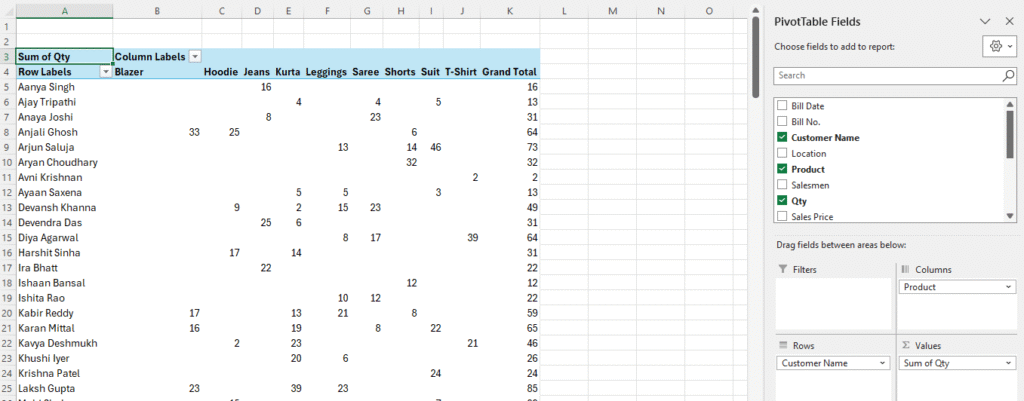
Example 3: Customer Purchase Summary
- Rows: Customer Name
- Columns: Product
- Values: Qty
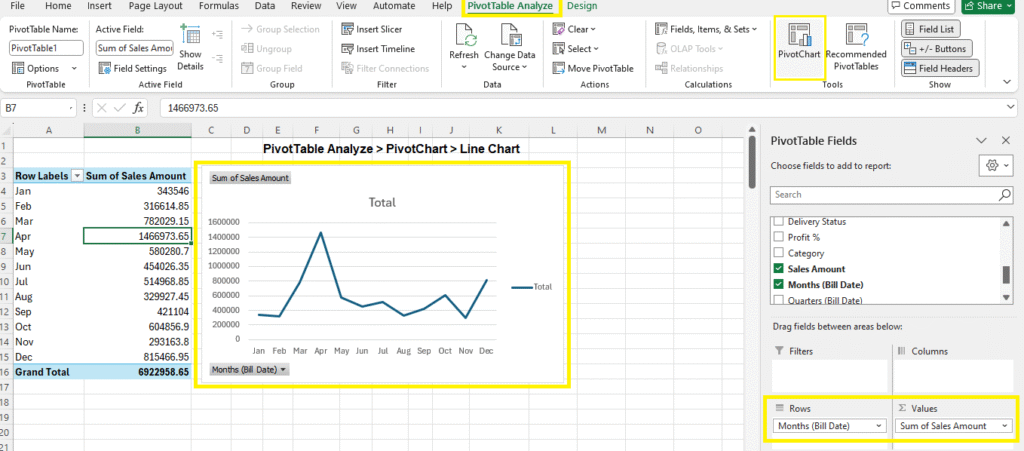
Example 4: Monthly Sales Trend
- Rows: Month (from Bill Date)
- Values: Sales Amount
- Show as Line Chart
Refresh Pivot Table (when Source Data Changes)
- When your source data changes, right-click the Pivot Table →
Refresh - To update automatically: Go to
PivotTable Options > Data > Refresh data when opening file
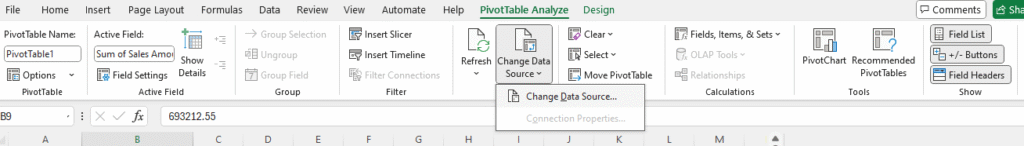
Change Data Source
Change Data Source lets you update the range of your Pivot Table when your original data grows or changes.
- Click on your Pivot Table
- PivotTable Analyze Tab > Change Data Source
- Select Data Range > OK
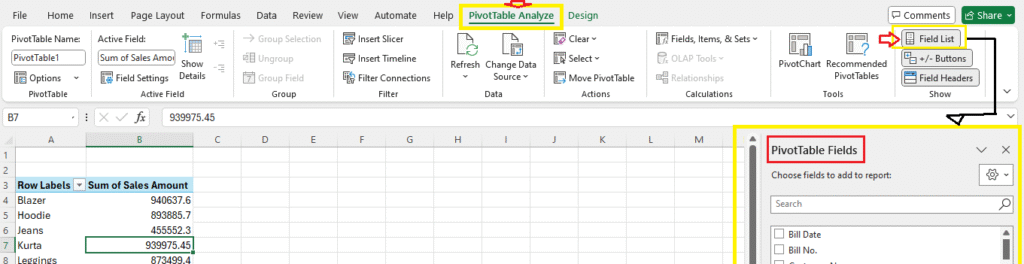
Hide/Unhide PivotTable Fields – Field List
Tips & Troubleshooting
- Always format source data as a Table before creating a Pivot
- Remove blank rows for accurate calculations
- Check for duplicates in headers
Download Practice Material
Summary
Pivot Tables are one of Excel’s best features for summarizing and analyzing data. From simple totals to advanced comparisons and filters, they save time and make reports dynamic.
Whether you’re managing sales, projects, or MIS reporting, Pivot Tables should be in your skillset.
FAQs – Pivot Table in Excel
Can I use Pivot Tables in Excel Online?
Yes, but features are limited compared to desktop Excel.
Will Pivot Tables update if I change the data?
Yes, but you need to click Refresh unless you set it to auto-refresh.
What is the difference between a Pivot Table and a regular table?
A regular table displays raw data, while a Pivot Table summarizes it dynamically.
Can I combine multiple sheets in a Pivot Table?
Yes, using Power Pivot or by combining data ranges.
Final Thoughts
Pivot Tables are not just for analysts — anyone working with Excel can use them to gain insights quickly. Start with basic summaries, and as your confidence grows, try out slicers, charts, and advanced calculations.
What’s Next?
In the next post, we’ll learn about the Error Handling in Excel